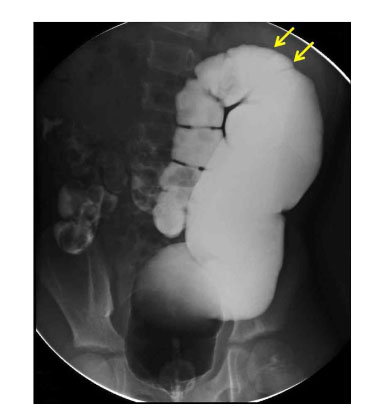
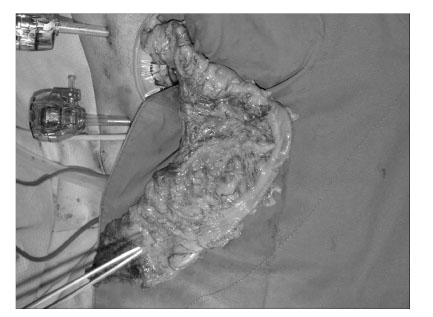
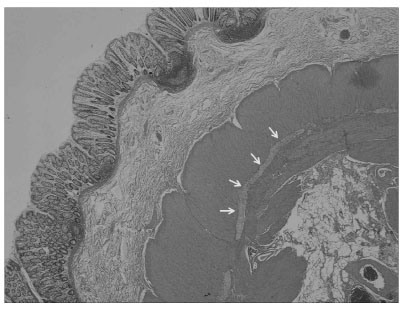
1Department of Pathology, Graduate school of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Taegu, Korea.
Department of Pediatric Surgery, Graduate school of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Taegu, Korea.
Copyright © 2013 Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons