Pediatric Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
1Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and GangNeung Asan Medical Center, GangNeung, Korea.
2Department of Pathology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2013 Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons
Values are presentated mean ± SD
Statistical significances were tested by Oneway analysis among group
Values are presentated mean ± SD or number
Statistical significances were tested by Oneway analysis among group
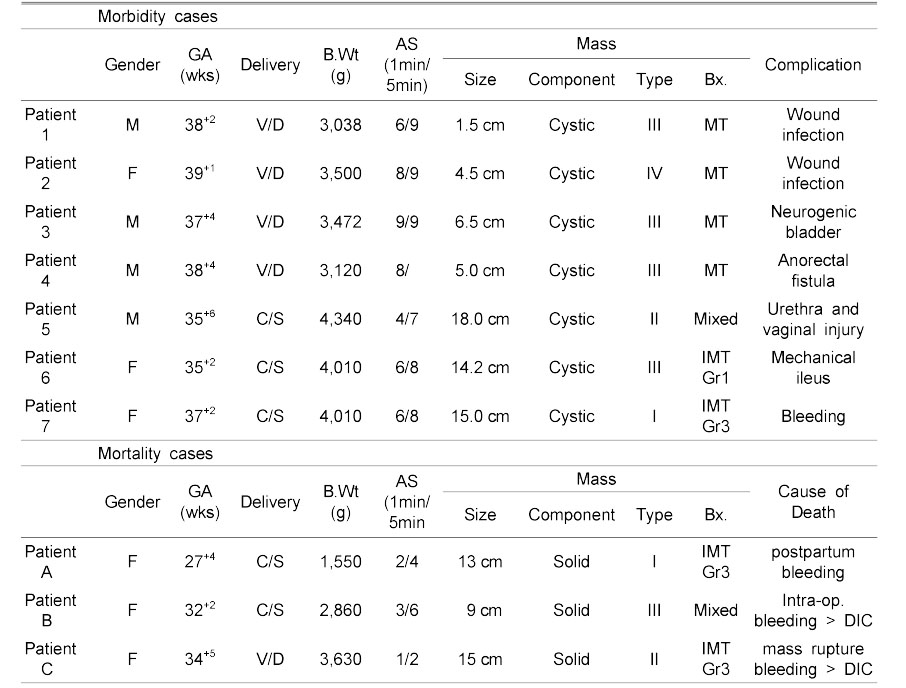
GA; Gestational Age, B.Wt; Birth Body Weight, V/D; Vaginal delivery, C/S; Caesarean section, AS; Apgar Score, Bx.; Biopsy (histological classification), IMT; Immature teratoma, MT; Mature teratoma, Gr; Grade, DIC; Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
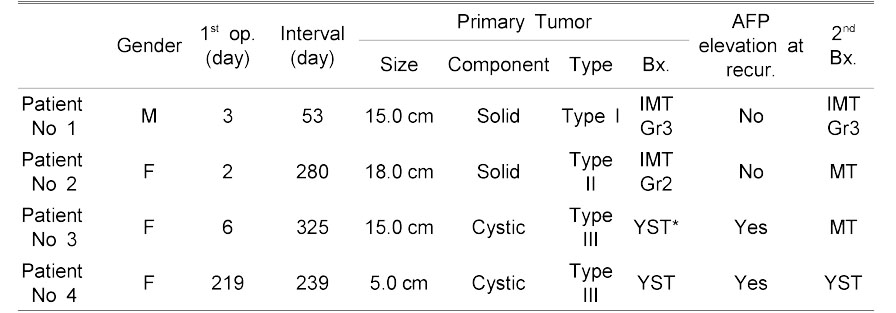
1st op. ; Age at 1st operation, Interval; The interval between first and second operation, Bx.; Biopsy(histological classification), 2nd Bx; The biopsy result of recurred tumor, MT; Mature teratoma, IMT; Immature teratoma, YST; York sac tumor, Gr; Grade
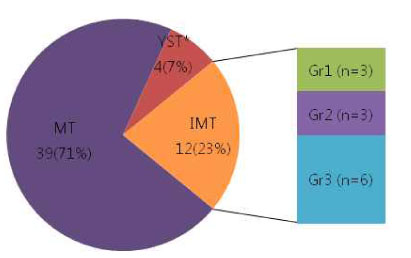
* IMT Gr3 40 %, MT 50 %, YST < 10 %
Demographics of the Patients
Values are presentated mean ± SD (range) or number (%)
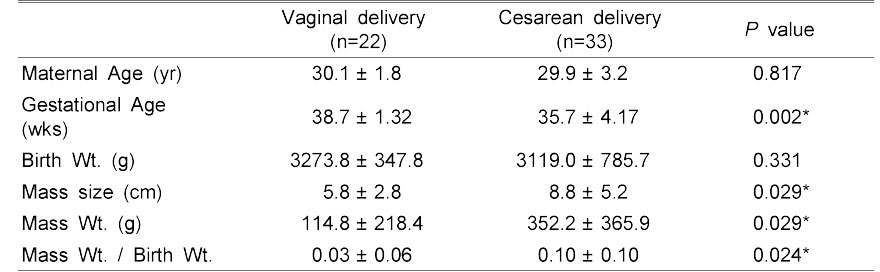
Route of Delivery (Vaginal vs. Cesarean delivery)
Values are presentated mean ± SD
Statistical significances were tested by Oneway analysis among group
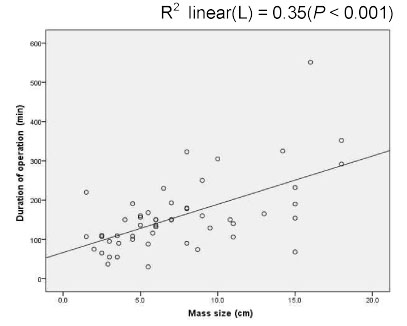
Gestational Age and Mass Size (P<0.001)
M; Mass size
Values are presentated number (%)
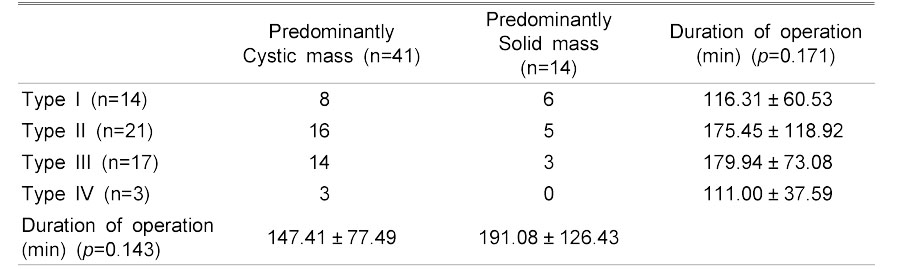
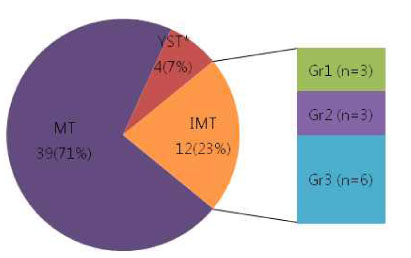
Types and Tumor Component and Duration of Operation
Values are presentated mean ± SD or number
Statistical significances were tested by Oneway analysis among group
Postoperative Morbidity and Mortality Cases of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma Patients
GA; Gestational Age, B.Wt; Birth Body Weight, V/D; Vaginal delivery, C/S; Caesarean section, AS; Apgar Score, Bx.; Biopsy (histological classification), IMT; Immature teratoma, MT; Mature teratoma, Gr; Grade, DIC; Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
Recurrence Cases of Sacrococcygeal Teratoma Patients
1st op. ; Age at 1st operation, Interval; The interval between first and second operation, Bx.; Biopsy(histological classification), 2nd Bx; The biopsy result of recurred tumor, MT; Mature teratoma, IMT; Immature teratoma, YST; York sac tumor, Gr; Grade
* IMT Gr3 40 %, MT 50 %, YST < 10 %
Values are presentated mean ± SD (range) or number (%)
Values are presentated mean ± SD
Statistical significances were tested by Oneway analysis among group
M; Mass size
Values are presentated number (%)
Values are presentated mean ± SD or number
Statistical significances were tested by Oneway analysis among group
GA; Gestational Age, B.Wt; Birth Body Weight, V/D; Vaginal delivery, C/S; Caesarean section, AS; Apgar Score, Bx.; Biopsy (histological classification), IMT; Immature teratoma, MT; Mature teratoma, Gr; Grade, DIC; Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation
1st op. ; Age at 1st operation, Interval; The interval between first and second operation, Bx.; Biopsy(histological classification), 2nd Bx; The biopsy result of recurred tumor, MT; Mature teratoma, IMT; Immature teratoma, YST; York sac tumor, Gr; Grade
* IMT Gr3 40 %, MT 50 %, YST < 10 %