Department of Pediatric Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2014 by the Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Demographic Data of of HPS Patients
Values are presented as ratio or median (range).
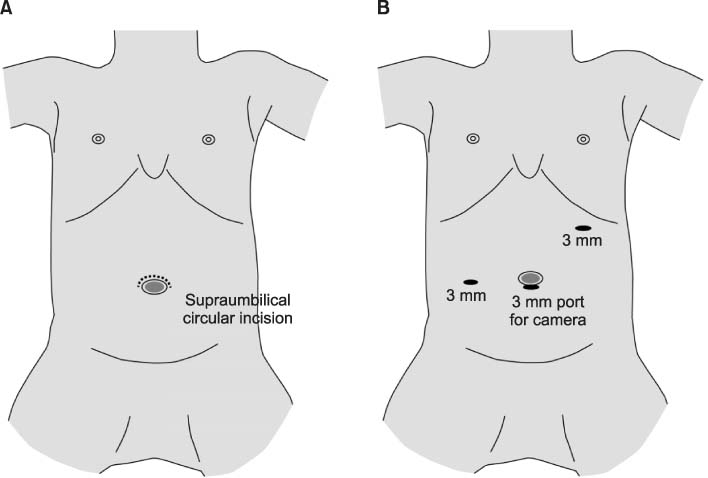
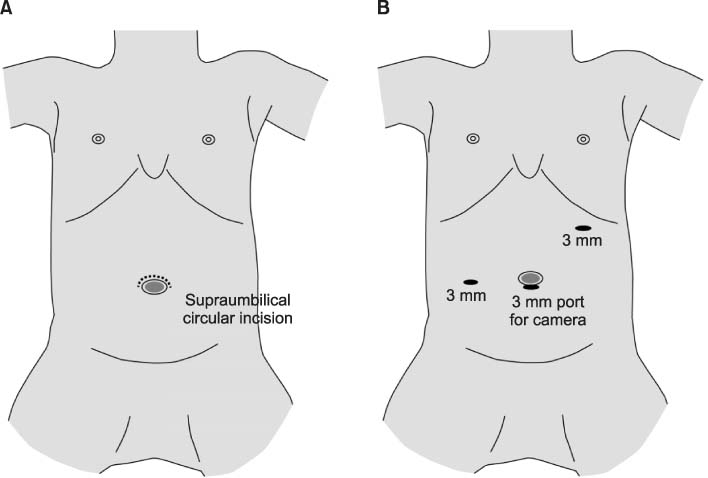
HPS, hypertrophic pyloric stenosis; OP, open pyloromyotomy (supraumbilical incision); LP, laparoscopic pyloromyotomy.
Clinical Outcomes Treated by OP or LP of Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis
Values are presented as median (range), n (%), or mean±SD.
OP, open pyloromyotomy (supraumbilical incision); LP, laparoscopic pyloromyotomy.
Values are presented as ratio or median (range).
HPS, hypertrophic pyloric stenosis; OP, open pyloromyotomy (supraumbilical incision); LP, laparoscopic pyloromyotomy.
Values are presented as median (range), n (%), or mean±SD.
OP, open pyloromyotomy (supraumbilical incision); LP, laparoscopic pyloromyotomy.