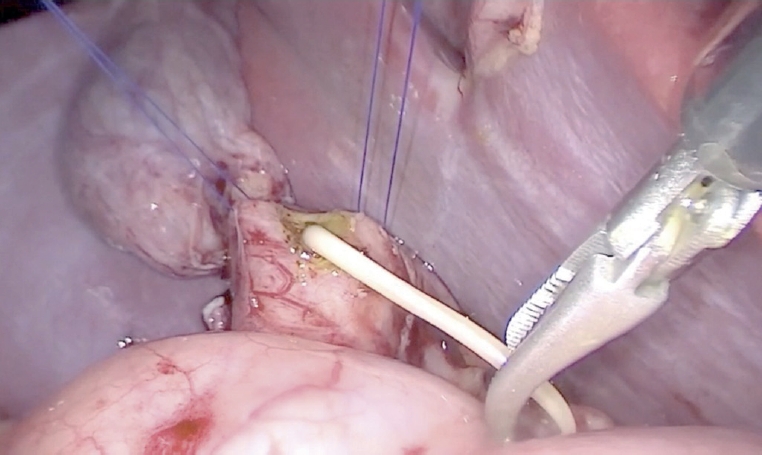
The congenital H-type rectovestibular fistula, a fistula between the anorectum and genital tract besides a normal anus is a rare variant of anorectal deformities. This disease needs proper treatment but there are no standard of diagnosis and treatment. The purpose of this report is to review a 13-year experience of approach and management for H-type rectovestibular fistula at a single institution.
From February 2002 to August 2015, we cared for 11 patients who had congenital H-type rectovestibular fistula and reviewed their clinical presentation, accompanied anomalies, diagnostic modalities, operative technique, and postoperative progress.
Most patients with H-type rectovestibular fistula presented with symptoms including vestibular defecation and major labial abscess. We could find the fistula tract in most of patients by fistulography using contrast dye. All of the patients had been operated. There were 2 recurrences after surgical treatment who had inflammation and infection associated with the fistula. All other patients recovered without complications.
We think the operation including fistulectomy and repair of perineal body through a transanal approach can be a feasible option to the congenital H-type rectovestibular fistula. Also, combined inflammation and infection should be treated prior to surgery to reduce postoperative complications.
Tuberculous Iliopsoas muscle abscess is a rare manifestation in patient with extrapulmonary tuberculosis and hardly observed in developed country. Paradoxical response to anti-tuberculous medication could make difficult therapeutic decision to clinicians. The authors report a case of tuberculous iliopsoas muscle abscess with multiple intraabdominal and thoracic abscesses in 9 year-old-boy who presented paradoxical response to anti-tuberculous treatment.
Use of laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) for perforated appendicitis (PA) in children remains controversial because of the development of postoperative intra-abdominal abscess formation. We developed the irrigation method for the prevention of abscess formation after LA performed for PA in children with severe panperitonitis. We called it ‘the shaking irrigation’. The object of this study was to analyze the efficacy of this irrigation method. All cases of PA with severe panperitonitis in children that underwent LA with massive shaking irrigation and drainage between June 2003 and December 2007 were studied retrospectively. We included only PA with panperitonitis and large amounts of purulent ascites throughout the abdomen as well as an inflamed small bowel with ileus. Thirty-four children were involved in this study. The mean patient age was eight years. The mean amount of irrigation fluid was 8.2L (range: 4-15L). The mean operative time was 89.5 min. The mean length of the hospital stay was 5.1 days. There were no postoperative intra-abdominal abscesses. There was no conversion to open surgery. In conclusion, Use of LA in PA with severe panperitonitis in children is safe and effective. Massive shaking irrigation and abdominal drainage appears to prevent intra-abdominal abscesses after LA for PA with panperitonitis.
Splenic abscess is a rare clinical condition with a reported incidence of 0.14 % to 0.70 % in various autopsy series. Primary tuberculosis of the spleen as a cause of splenic abscess is even rarer, especially in the antitubercular era. Infants and children have a higher predisposition to extra-pulmonary tuberculosis than adults and tend to develop severe extra-pulmonary disease such as miliary tuberculosis and meningitis. The diagnosis of tuberculosis in infants and children can be difficult because of nonspecific symptoms and clinical findings. Computed tomography establishes the diagnosis of splenic abscess and demonstrates the number and location of abscesses. Splenectomy is the standard of care in most clinical setting. We present a 4-year-old girl who had multiple tuberculosis splenic abscesses and was treated successfully with splenectomy.
To evaluate the clinical characteristics and results of treatment of fistula-in-ano and perianal abscess in childhood, we analyzed 95 cases of fistula-in-ano and/or perianal abscess seen in childhood, between January 1995 and June 2001 at the Department of General Surgery of Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital. Perianal abscess was in 25 patients, anal fistula in 62 and combined disease (perianal fistula and abscess) in 8. Male predominance was noted (95 %). Median age was 8 months and 78 % of cases were presented under the age of 1 year. Median duration of symptoms was 60 days. Twenty four abscesses (77 %) and 18 lesions (72 %) of combined disease (n=25) were located on both lateral sides of the anus, and fistulas located on both lateral sides were 33 (53 %). Multiplicity of the lesion was noted in 25 % of cases. Sixteen percent of abscess, 81 % of fistula and 88 % of combination group have had previous perianal abscesses. The perianal abscesses were treated with incision and curreTage and fistulas were treated with fistulotomy or fistulectomy. There were no recurrent diseases and no complications after surgical treatment. Although the progresses of the perianal abscess and fistula in ano in childhood may be self-limitied, surgical management was safe and curable.
The sacrococcygeal region is the frequent site for meningocele, congenital dermal sinus and pilonidal cyst. From May 1995 to July 1998, we have treated 8 neonatal patients with an abscess in the sacrococcygeal area. The mean age at onset was 8.3 days with a range from 6 to 11 days. The sex ratio was 5:3 with male preponderance. Mild fever was the only systemic symptom. Ultrasonogram revealed a slightly hypo echoic lesion in the subcutaneous tissue which became more hypoechoic with time. Pus cultures showed
Anal fistula and perianal abscess in pediatric patients have been reported to have several characteristics, e.g. prevalent in less than 2 years of age, male preponderence, straight course of tract, and low type of fistula. We performed a retrospective study of twenty nine pediatric patients to see these characteristics comparing with the transitional age group of adolescents. Between June 1989 and December 1993, twenty-nine pediatric (<15 year-old) and sixteen adolescent patients(≥ 15, < 25 year-old) with anal fistula and perianal abscess were treated by surgical intervention. Twenty-one(87.5%) and 10(66.7%) enteric bacterial colonies were isolated from 16 pediatric and 11 adolescent patients, respectively. Considering the predominance of low type and the organisms cultured in the pediatric group, crypt-glandular infection seems to be a major preceding event. Incision and drainage were sufficient for cure in 15 among 16 perianal abscesses, and fistulas were cured by either fistulotomy or fistulectomy in all the 14 patients. The importance of effective drainage of perianal abscess and fistulotomy including internal opening cannot be overemphasized.

