A baby was diagnosed with esophageal atresia (EA) with tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) on the next day after birth, and end-to-end anastomosis of esophagus with TEF ligation was performed. The distance between proximal and distal esophageal pouch was checked as 3 vertebral body lengths and a 1 cm-sized bronchogenic cyst (BC) was identified near carina on the right side, just below the proximal esophageal pouch. This case report described the baby who have a BC was located between the both esophageal pouch and a longer esophageal gap than usual EA with distal TEF.
Citations

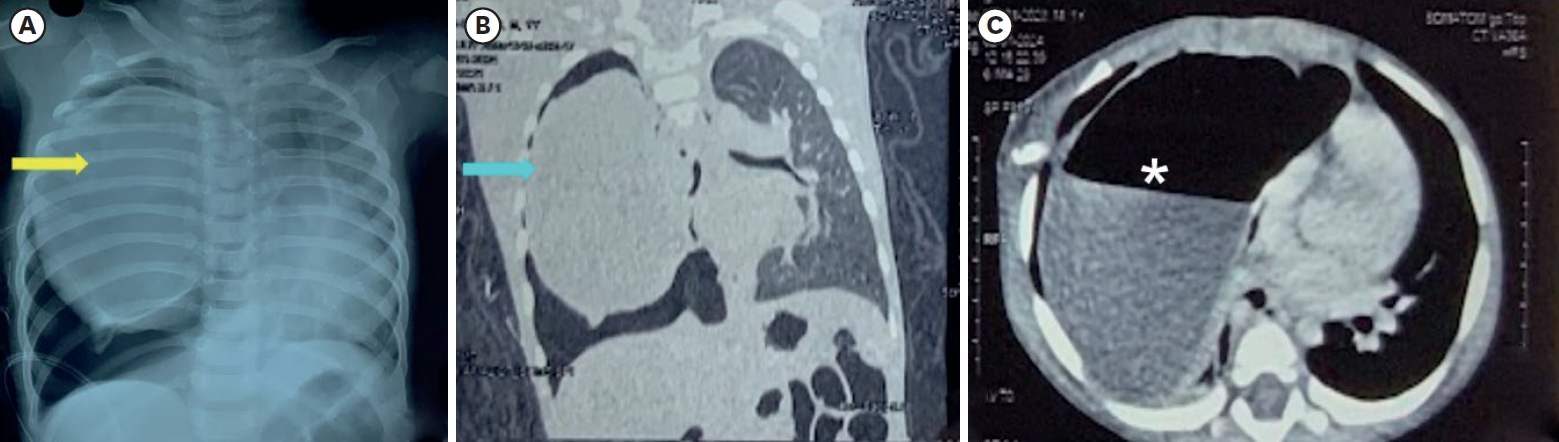
A 19-month-old boy suffered from stridor and dysphagia. He was taking asthma medication for a few months, but symptoms did not improve. After admission, a chest CT showed a posterior mediastinal mass, which compressed the trachea and esophagus. The removed mass via open thoracotomy was a bronchogenic cyst on histopathology. Postoperatively, stridor and dysphagia disappeared. In case of persistent and refractory stridor or dysphagia in children, congenital lesions including bronchogenic cyst need to be ruled out.

