Citations

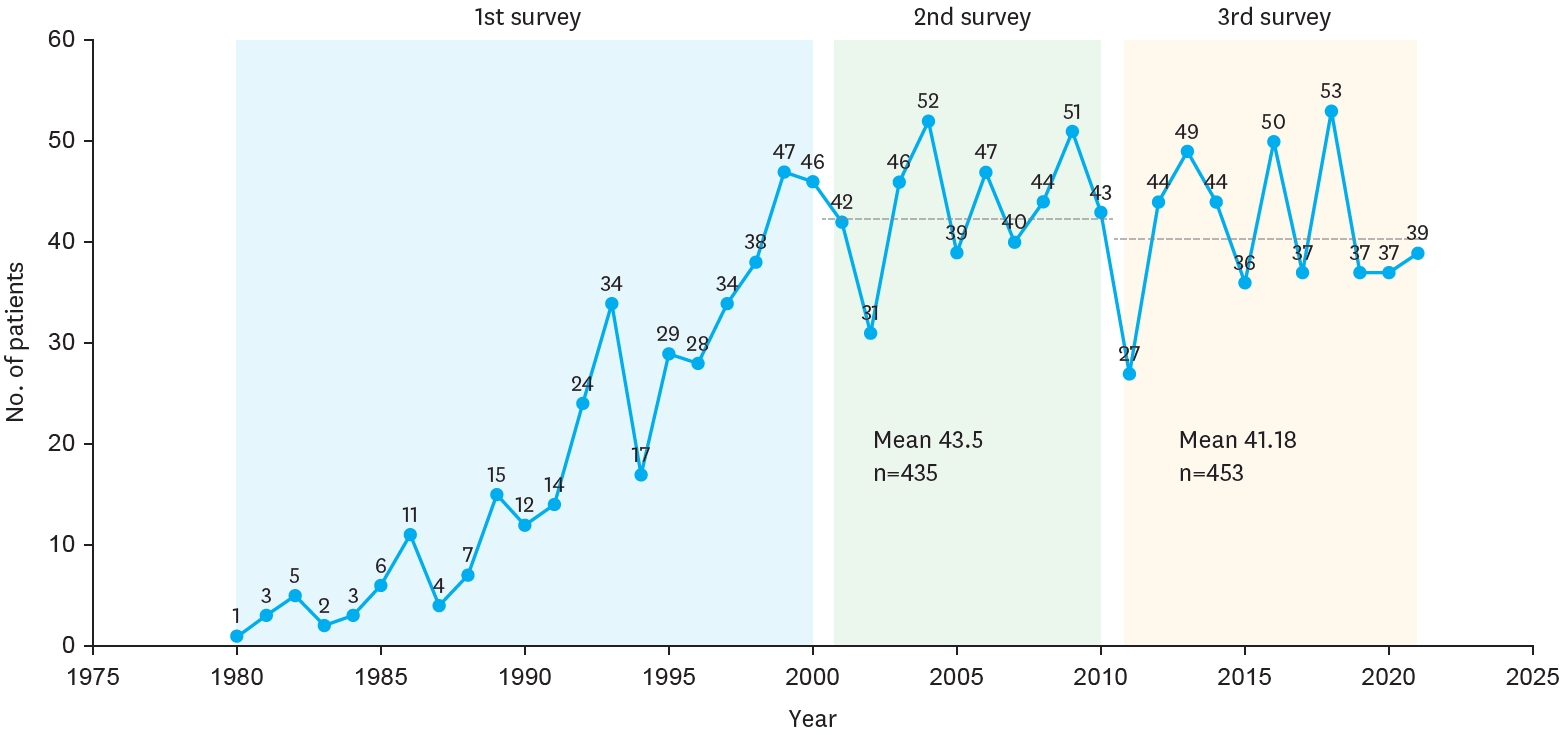
The Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons (KAPS) performed the second nationwide survey on biliary atresia in 2011. It was a follow-up study to the first survey, which was performed in 2001 for the retrospective analysis of biliary atresia between 1980 and 2000. In the second survey, the authors reviewed and analyzed the clinical data of patients who were treated for biliary atresia by the members of KAPS from 2001 to 2010. A total of 459 patients were registered. Among them, 435 patients primarily underwent the Kasai operation. The mean age of patients who underwent the Kasai operation was 66.2±28.7 days, and 89.7% of those patients had type III biliary atresia. Only five patients (1.4%) had complications related to the Kasai operation. After the Kasai operation, 269 (61.8%) of the patients were re-admitted because of cholangitis (79.9%) and varices (20.4%). One hundred and fifty-nine (36.6%) of the patients who underwent the Kasai operation subsequently underwent liver transplantation. The most common cause of subsequent liver transplantation was persistent hyperbilirubinemia. The mean interval between the Kasai operation and liver transplantation was 1.1±1.3 years. Overall the 10-year survival rate after the Kasai operation was 92.9% and the 10-year native liver survival rate was 59.8%. We had 23 patients for primary liver transplantation without the Kasai operation. The mean age patients who underwent primary liver transplantation was 8.6±2.9 months. In summary, among the 458 Kasai-operation and liver-transplantation patients, 373 lived, 31 died, and 54 were unavailable for follow up. One-third of the patient who survived have had complications correlated with biliary atresia. In comparison with the first survey, this study showed a higher survival rate and a greater number of liver transplantation.
Citations

The purpose of this study is to analyse clinical impact of specific MRI findings in liver in patients of long-term survivors after Kasai portoenterostomy (KPE). Twenty-eight patients who were underwent KPE were followed up more than 5 years. Macro-regenerative nodule (MRN) and beaded-duct dilatation (BDD) were considered as important findings in liver MRI. The association between these findings in MRI and clinical indicator, serum bilirubin level and history of cholangitis were evaluated. Sixteen patients (57.1%) were shown MRN in liver MRI. There were 14 patients(50%) whose MRI showed BDD. Serum total and direct bilirubin were 3.6mg/dL and 1.8mg/dL respectively in positive MRN group whereas 1.4mg/dL and 0.7mg/dL in negative MRN group (
Biliary atresia (BA) is an infantile cholestatic disease of progressive obliterative cholangiopathy with varying degrees of damage to both extra and intrahepatic bile ducts due to unknown causes. The diagnostic studies should be done to diagnose or exclude BA without unnecessary delay. Kasai portoenterostomy is the first choice of treatment for bile drainage from microscopic bile ductules present in the portal fibrous mass. The medical management after Kasai portoenterostomy should be done carefully to maintain bile excretion and prevent and treat complications including cholangitis, hepatic fibrosis, portal hypertension and nutritional problem. The reported five years-survival rates after Kasai portoenterostomy range from 30 to 60%. About 20% of all patients undergoing Kasai portoenterostomy during infancy survive into adulthood with their native liver. Even if Kasai portoenterostomy remains as the first line of treatment in BA, liver transplantation serves as a good salvage treatment when portoenterostomy fails or liver function gradually deteriorates after initially successful establishment of bile flow. Overall 5-year survival rate in BA is about 90% in recent series.
To evaluate the long-term prognosis of biliary atresia after Kasai operation, a total of 14 patients (of the 41 patients operated upon from 1982 to 1997), who had been followed up for more than 10 years, were included in this retrospective study. Eleven out of 14 patients survived with their native livers, and their data analyzed for age at operation, clearing time of jaundice, histological outcome, postoperative complications, effectiveness after the application of an intussusception anti-reflex valve, and quality of life. Average age at surgery was 62.8 days. Serum bilirubin was normalized within three months in all patients. Six among the eleven long-term survivors had ascending cholangitis as one of the postoperative complications. The application of an intussusception anti-reflux valve did not show any statistical significance in long-term survival. Most of long-term survivors appeared to enjoy good quality of life. Kasai operation might not be the definitive treatment for biliary atresia; however, Kasai operation made it possible to achieve long-term survival for patients with biliary atresia when the patients were detected and treated as early as possible.
Biliary atresia (BA) is an uncommon neonatal surgical disease that has a fatal outcome if not properly treated. The survival rates of the patients with native liver after Kasai's operation in countries outside Japan are not so good. We reviewed the results of 22 cases of biliary atresia treated in Kosin University Hospital between October 1987 and March 2001. There were 13 males and 9 females aged from 21 to 106 days (mean 52 days). There were 3 cases of Type I (13.6%), and 3 of Type II (13.6%), and 16 Type III (72.7%). The operative methods were resection of the common bile duct remnant and cyst followed by Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy in 3 cases for Type I BA; Kasai I in 15 cases, Kasai II in 1 case, and Ueda's operation in 3 cases for Types II and III BA. There was no death within the first 30 days after operation. We were able to follow 21 of the 22 patients (95.4%) for more than 5 years. The actual 5 year survival rate (YSR) was 40.9%. One Type I case received a living-related liver transplantation at 6 years of age because of the multiple intrahepatic stones and liver cirrhosis. Five YSR after biliostomy group (Kasai II and Ueda op.) was 75% (3/4) while that of Kasai I was 20% (3/15). One case had no bile duct in the resected fibrotic plaque on microscopic review and died 8 months after Kasai I operation, would have been a strong candidate for early liver transplantation. From the above result, our conclusions are as follows; (1) early liver transplantation should be considered for cases of no bile duct after pathologic examination of the resected specimen, (2) measures to prevent postoperative cholangitis and prevention of postoperative liver cirrhosis are needed, (3) liver transplantation program should be available for failed cases.
Biliary atresia (BA) is the result of fibrosing destructive inflammatory process affecting intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts, which lead to cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Kasai portoenterostomy has been the standard operative procedure in biliary atresia. Recently, there has been remarkable increase in the survival rate in cases of BA. However, long-term survivors are not clearly evaluated in Korea. To define long-term prognosis factors of patients who underwent surgery for BA, a retrospective study was undertaken of 10 (37 %) patients surviving more than 10 years among 27 patients who underwent one of Kasai procedures between 1981 and 1995. Hepatomegaly was present in 4 and splenomegaly in 7 patients. Serum bilirubin was normalized at 1 year after operation. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT), Alanine aminotransferase(ALT, GPT) were normalized at 12 years and alkaline phosphatase(ALP) was normalized at 13.5 years. Cholangitis developed mainly within 5 years after operation so close follow up is needed. Life long follow-up is needed because of progressive deterioration of liver function even after 10 years.
The prognostic factors for extrahepatic biliary atresia (EHBA) after Kasai portoenterostomy include the patient's age at portoenterostomy (age), size of bile duct in theporta hepatis (size), clearance of jaundice after operation (clearance) and the surgeon's experience. The aim of this study is to examine the most significant prognostic factor of EHBA after Kasai portoenterostomy. This retrospective study was done in 51 cases of EHBA that received Kasai portoenterostomy by one pediatric surgeon. For the statistical analysis, Kaplan-Meier method, Logrank test and Cox regression test were used. A
Citations

Biliary atresia (BA) with extrahepatic biliary cysts (EHBC) is a rare disease. It has been generally recognized as type I (correctable with cystic dilatation), which means a good prognosis. From a total of 73 patients with BA who underwent operation from September 1988 to September 2003 at our institute, 7 (9.6 %) cases of type III BA with EHBC (uncorrectable with cystic dilatation) are reviewed. Clinical findings, laboratory data, radiologic findings, treatment methods and outcomes were reviewed. Female was more prevalent (male to female ratio; 2:5). All cases were type III with EHBC according to the intraoperative cholangiography, and underwent Kasai's portoenterostomy. The mean age was 57 days at operation. Three patients(42.9 %) are long term survivors. Further evaluation is needed to determine the correlation between prognostic factors and outcome for.
When jaundice persists for more than 14 days postnatally, the early diagnosis of surgical jaundice is important for the prognosis in extrahepatic biliary atresia after draining procedure. The role of diagnostic laparoscopy to differenctiate medical causes of jaundice from biliary atresia is evaluated in this report. Four patients with prolonged jaundice have been included in this study. When the gallbladder was not visualized we proceeded to laparotomy. In patients with enlarged gallbladder visualized at laparoscopy, laparoscopic guided cholangiogram was performed, and laparoscopic liver biopsy was done for those who had a patent biliary tree. Two patients had small atretic gallbladder and underwent a Kasai hepato-portoenterostomy. One patients showed a patent gallbladder and common bile duct with atresia of the common hepatic and intrahepatic ducts, and they underwent a Kasai hepatic-portoenterostomy. One patient showed an enlarged gallbladder and laparoscopic-guided cholangiogram were normal. Laparoscopic liver biopsy was performed. There were no complications. Laparoscopy wth laparoscopic-guided cholangiogram may be a valuable method in accurate and earlier diagnosis in an infant with prolonged jaundice.
A survey on biliary atresia was made among 26 members of the Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons. The members were required to complete a questionnaire and a case registration form for each patient during the twentyone-year period of 1980-2000. Three hundred and eighty patients were registered from 18 institutions. The average number of patients per surgeon was one to two every year. The male to female ratio was 1 : 1.3. The age of patients on diagnosis with biliary atresia was on average 65.4 ±36.2 days old. The national distribution was 32.8% in Seoul, 25.3% in Gyoungki-Do, 21.6% in Gyoungsang-Do, 9.27% in Choongchung-Do, etc. in order. The most common clinical presentation was jaundice (98.4%) and change of stool color (86.2%) was second. Two hundred eighty (74.7%) of 375 patients were operated by 80 days of age. Three hundred thirty six (91.9%) of 366 patients were operated on by the original Kasai procedure, and 305 (84.3%) of 362 patients were observed by bile-drainage postoperatively. The overall postoperative complication rate was 18.5% and the overall postoperative mortality rate was 6.8%. The associated anomalies were observed in 72 cases (22.5%). One hundred ninty five (64.7%) of 302 patients have been alive in follow-up and 49 (25.1%) have survived over 5 years without problem after operation. Ascending cholangitis, varices and ascites affected survival significantly, and the important long-term prognostic factor was the occurrence of complications.
Citations

This paper includes our 9-year experience of 34 infants with biliary atresia with introduction of a new non-invasive diagnostic method, that is, ultrasonographic "triangular cord" (TC) sign. TC sign was defined as visualization of a triangular or a band-like echogenicity just cranial to the portal vein. Ultrasonographic TC sign seemed to be a simple, non-invasive, time-saving and useful tool in the diagnosis of biliary atresia, representing 84% sensitivity. Active bile excretion was restored in 90% of the patients who were treated between 31-60days, 78% of those between 61-90 days, and 33% of those being 91days or older. The incidence of postoperative cholangitis was 36%, and construction of antireflux valve in the Roux-en -Y loop did not affect the incidence of postoperative cholangitis (P=0.18). As for the surgical outcome, of 34 infants with biliary atresia, 23 (68%) are alive for 2-102 months period, and 12 of them are alive for more than 5 years . Five-year estimate survival by Kaplan-Meier method was 66 %.
Citations

A 6(1/2)-year-old girl developed recurrent cholangitis following hepatic portoenterostomy for biliary atresia. Computed tomogram showed an ovoid cyst (4.5 × 4.0 cm in size) in the left hepatic lobe and another tubular dilatation (2.0 × 0.8 cm in size) in the right hepatic lobe. Percutaneous transhepatic cholangio-drainage (PTCD) with cystogram showed an ovoid cyst in the left hepatic lobe (Tsuchida type A), measuring 6.6 × 5.0 cmin size. She became afebrile and anicteric with aid of PTCD and parenteral antibiotics. However she continued to drain 45-150 cc of bile per day via the tube for over 2 weeks. Then she successfully underwent intrahepatic cystojejunostomy with guidance of intraoperative ultrasonography. This case illustrates relapsing cholangitis caused by Tsuchida type A intrahepatic cyst, which was successfully managed with PTCD followed by internal drainage procedure.
Citations

The results of hepatic portojejunostomy in 34 patients with biliary atresia operated upon by one surgeon between May 1989 and December 1997 were analyzed. Eleven (32.3 %) patients were 60 days or younger, 14 patient (41.2 %) were between 60 and 90 days, and 9 (26.5 %) were over 90 days of age. Jaundice cleared in 20 cases (58.8 %). Three patients died of liver insufficiency, 2 were anicteric but died from esophageal variceal bleeding. Three patients died as a result of sepsis, heart failure and left kidney agenesis. Five patients were lost to follow-up. The five-year survival rate was 73.8 %. Two patients over 90 days of age, survived more than 5 years. Survival rates were not significantly related to the age at operation. We conclude that hepatic portojejunostomy should be considered as a primary surgical modality for biliary atresia, even at age 90 days or more. Early detection of esophageal varices and sclerotherapy may be necessary. Liver transplantation is necessary if hepatic failure develops.
To assess the clinical and nutritional status of long-term survivors of biliary atresia, history taking, medical record review, physical examination (height, weight, MAC, TSF), blood tests (LFT, prothrombin time, platelet count, prealbumin, calcium) and liver needle biopsy were performed in 12 patients in whom Kasai procedure were performed more than 10 years ago at Department of Pediatric Surgery in Seoul National University Hospital. None were below the 5th percentile in height and weight. TSF was above the 75th percentile in all patients and showed good subcutaneous fat deposition. MAC was above the 5th percentile in all patients. Serum prealbumin level was abnormal in 2 patients with abnormal liver function and revealed visceral protein malnutrition. Serum calcium level was decreased below normal range in 4 patients with abnormal liver function. One patient had mild ascites. Five patients had abnormal liver function and 7 patients showed clinical manifestation of portal hypertension. Liver needle biopsy was performed in 5 patients and no cirrhotic change was observed. Although some patients who have survived for more than 10 years after Kasai procedure developed protein malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies, growth and development and nutritional status were generally satisfactory. Five patients(42%) showed normal liver function and no portal hypertension. In conclusion, Kasai procedure is satisfactory as a primary treatment in biliary atresia but significant portion of long-term survivors had abnormal liver function and portal hypertension. Continuous and careful follow-up is necessary to determine when liver transplantation may be indicated.
Extended porta hepatis dissection and hepatic porto jejunostomy was performed on 14 biliary atresia patients during last 13 years by a single surgeon. The average age at operation was 68 days(range from 37 days to 98 days). The patients were admitted for 8 weeks postoperatively for administration of parenteral antibiotics. There was one operative mortality due to acute hepatic necrosis. Among 13 patients remaining, 12(92.5 %) became chemically jaundice-free within 36 weeks postoperatively(average 16.8 weeks), the earliest 8 weeks, and in one patients jaundice persisted. Five( 38.5 %) patients developed cholangitis after operation. Among jaundice-free patients, one patient died of unrelated disease 2 years after hepatic porto jejunostomy, who underwent left lateral segmentectomy because of a biloma. Eleven survivors(78.6 %) are jaundice-free. The oldest one is 13 years old, enjoying a normal life. The mean period of follow-up is 7 years and 3 months.
To differentiate biliary atresia from intraheaptic cholestasis, Tc-99m DISIDA hepatobiliary scintigraphies and percutaneous needle biopsies of 60 consecutive infants were evaluated retrospectively. Twenty three patients had biliary atresia and 37 patients intraheaptic cholestasis(neonatal hepatitis 34, TPN induced jaundice 2 and Dubin-Johnson syndrome i). All sixty patients underwent Tc-99m DISIDA hepatobiliary scintigraphy with phenobarbital pretreatment. Of 23 patients with biliary atresia, 22 were correctly interpreted showing 96% sensitivity while of 37 patients with intraheaptic cholestasis, only 12 had intestinal excretion of radionudide showing 32% specificity. Among the forty needle biopsies, 17 of biliary atresia and 23 of intrahepatic cholestasis, 37 were correctly interpreted as either having biliary atresia or intrahepatic cholestasis. The overall diagnostic accuracy was 93%. Of 3 misdiagnosed cases, the histologic findings of two patients with biliary atresia(aged 43 days and 54 days at the first needle biopsy) were essentially the same as those of neonatal hepatitis. Follow-up biopsies, however, showed findings consistent with biliary atresia. The third one(VLBW premie with history of 8 weeks of TPN) showed mild ductal proliferation and portal fibrosis. This was interpreted as suspicious for biliary atresia. Jaundice resolved gradually. In summary, patients who have intestinal excretion of radionudide on Tc-99m DISIDA hepatobiliary scintigraphy, biliary atresia can be ruled out. But the patients who do not have intestinal excretion of radionudide should have further investigation by needle biopsy. Judicious use of Tc-99m DISIDA hepatobiliary scintigraphy and percutaneous needle biopsy can give a diagnostic accuracy of 95% or more in cases of infantile cholestasis.
Citations

Although bleeding was reported before as the first symptom in a few cases of biliary atresia, this association is not generally known. We treated 115-day-old female with extrahepatic biliary atresia presented with subdural hemorrhage rather than with prolonged jaundice. Four years after craniectomy and Kasai's hepatic portojejunostomy, she looks happy without jaundice nor brain damage sequela even though she had recent episode of esophageal variceal bleeding.
Citations

Citations


