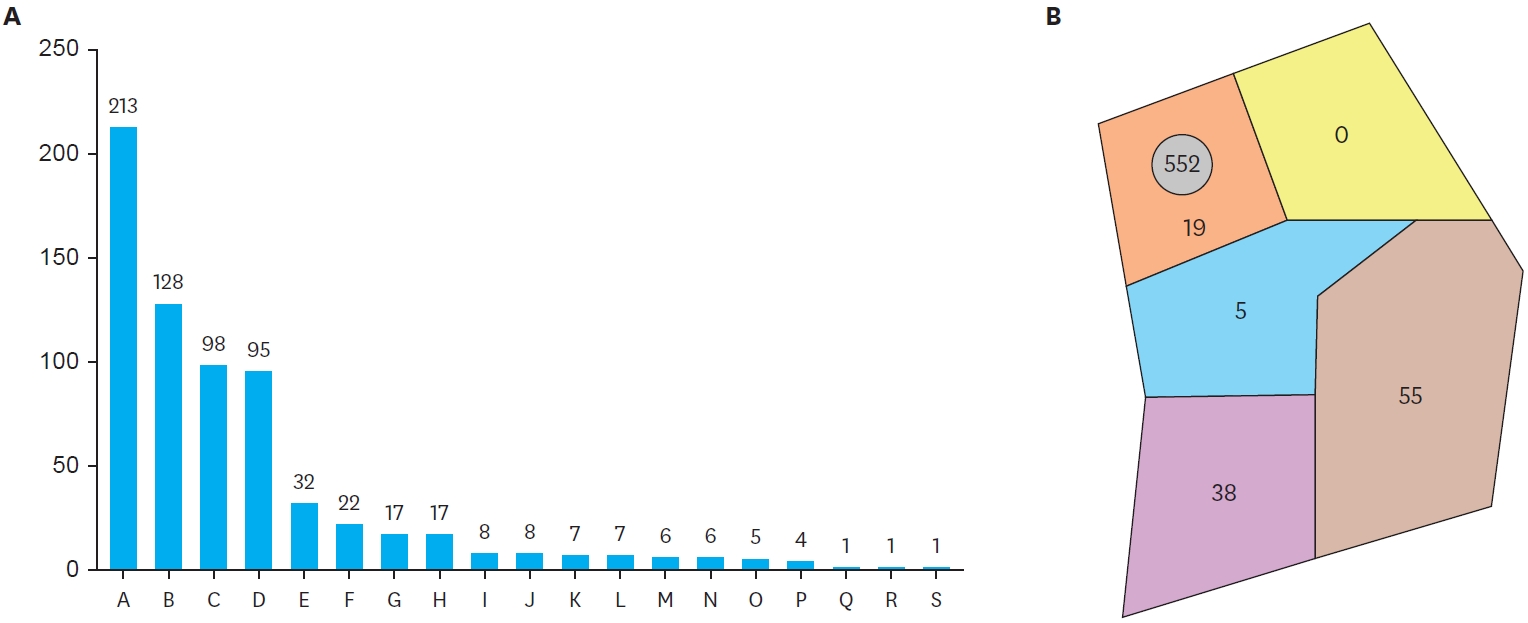
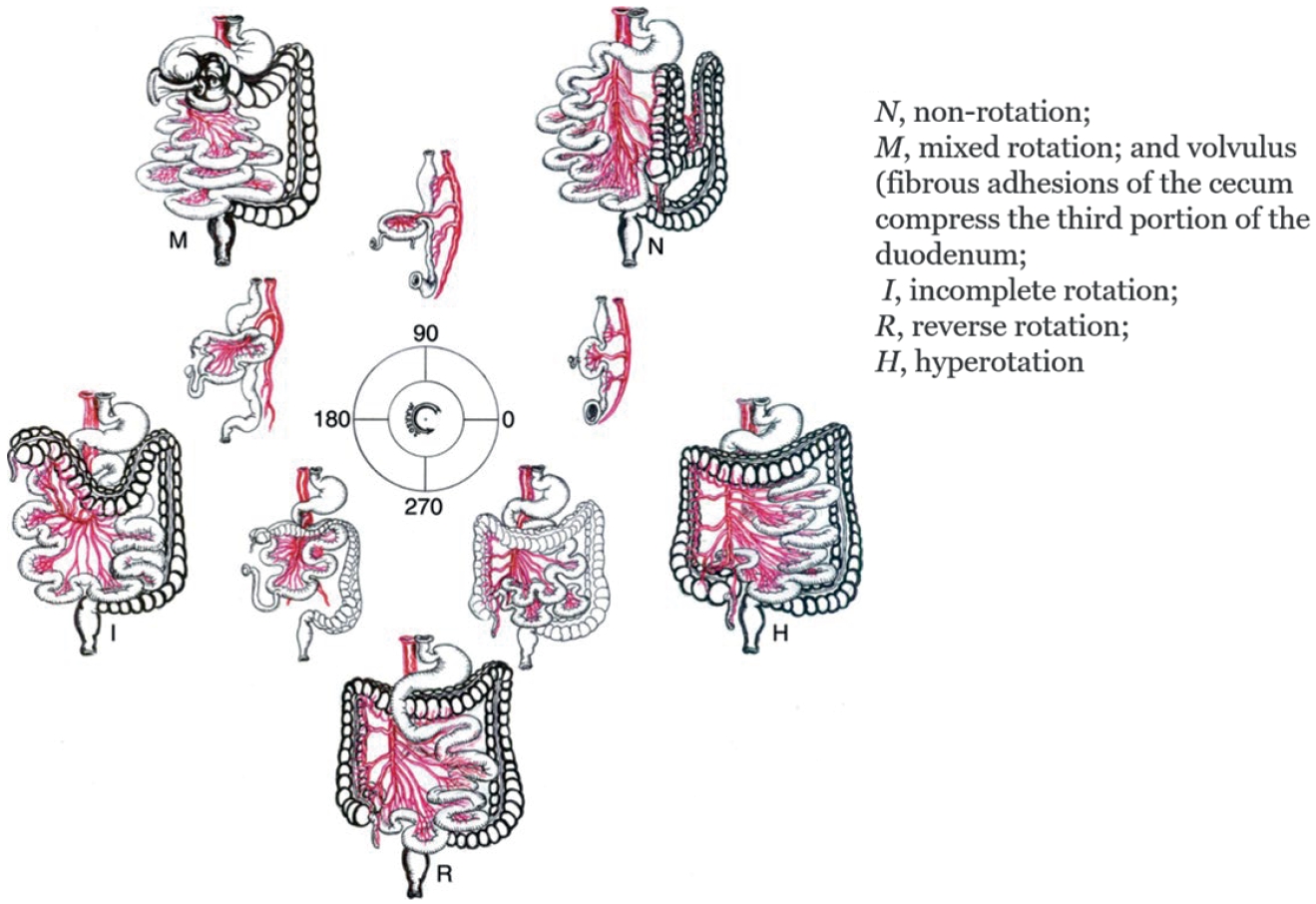
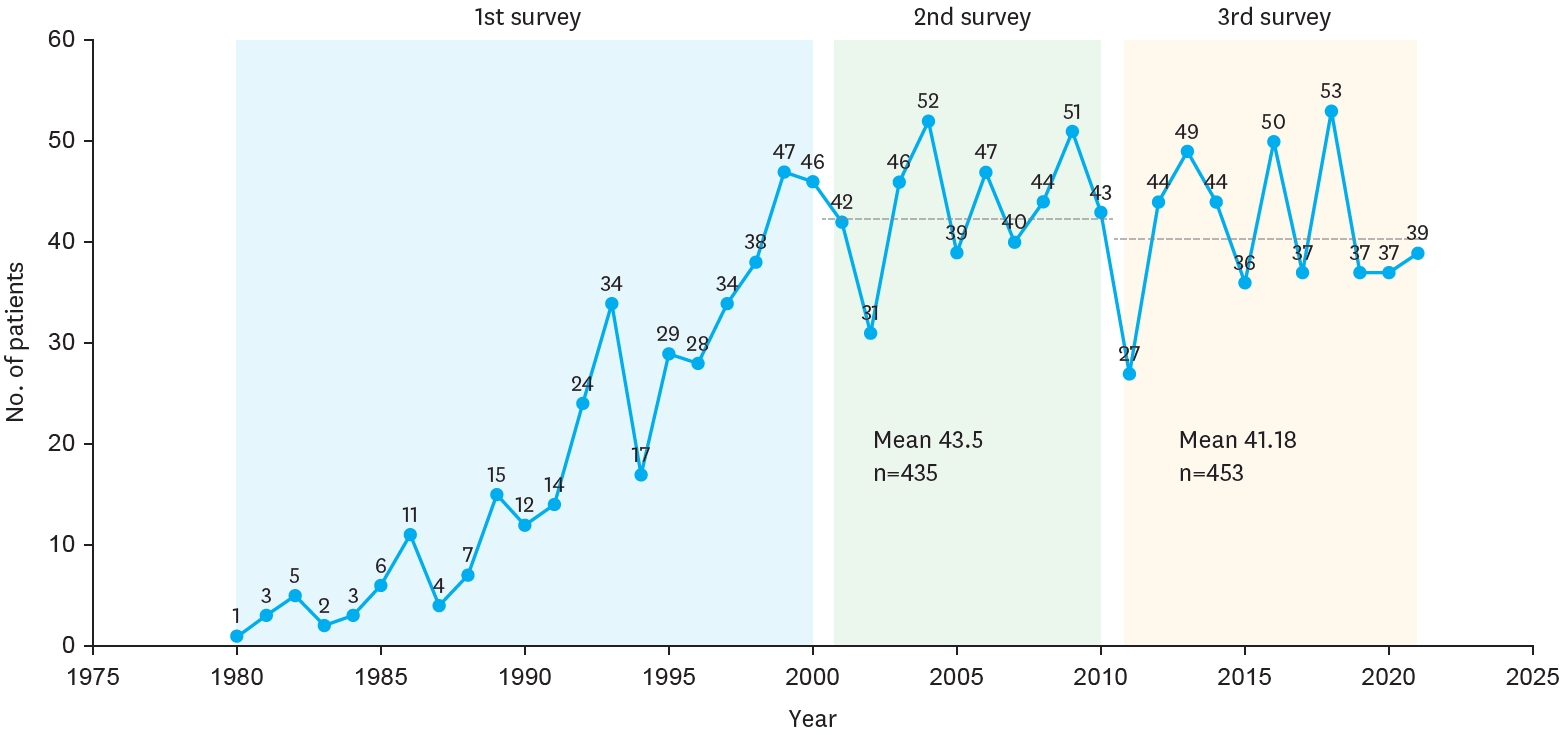
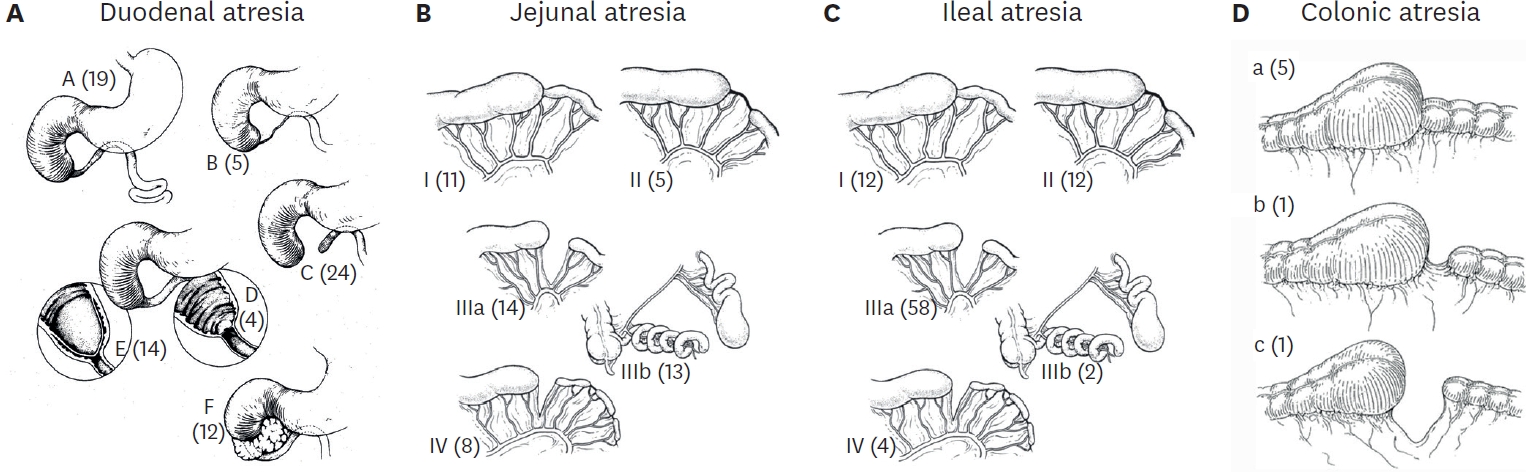
The Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons (KAPS) performed a nationwide survey on sacrococcygeal teratoma in 2018.
The authors reviewed and analyzed the clinical data of patients who had been treated for sacrococcygeal teratoma by KAPS members from 2008 to 2017.
A total of 189 patients from 18 institutes were registered for the study, which was the first national survey of this disease dealing with a large number of patients in Korea. The results were discussed at the 34th annual meeting of KAPS, which was held in Jeonju on June 21–22, 2018.
We believe that this study could be utilized as a guideline for the treatment of sacrococcygeal teratoma to diminish pediatric surgeons' difficulties in treating this disease and thus lead to better outcomes.
Citations

Single-port laparoscopy-assisted surgery is being performed for various operations in pediatric patients recently. The aims of this study were to prove the safety and find well-matched indications of small bowel resection using single-site umbilical laparoscopic surgery (SSULS).
From 2011 to 2016, 29 pediatric patients underwent SSULS. Medical records were retrospectively reviewed.
A total of 29 patients were included and 30 SSULS were performed in this study. The mean age at operation was 5.7 years, and the mean weight was 21.9 kg. Meckel's diverticulum was the most common indication for SSULS, followed by small bowel intussusception due to leading point mass, small bowel duplication, and Crohn's disease. In most cases, estimated blood loss was negligible except in Crohn's disease with severe inflammation. While answering post-discharge questions about scars, most parents responded that they were satisfied with the postoperative wound.
SSULS is a useful operation to try even for surgeons who do not have advanced laparoscopic skills. Complication rates of single-port operations do not differ from those of conventional laparoscopic operations. Most lesions of the small bowel could be indications of SSULS. Careful attention is required when performing SSULS in patients with Crohn's disease.
Citations

Total proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (T-IPAA) in childhood is a surgical procedure mainly applied to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or ulcerative colitis (UC), but it can be applied to non-FAP/non-UC disease (NFNU). Studies regarding the role of T-IPAA who underwent the operation in childhood, especially in terms of long-term gastrointestinal function, complications, and quality of life (QOL) are limited. The aim of this study was to evaluate the characteristics of patients receiving T-IPAA and to compare their bowel function outcomes and QOL.
Patients aged ≤18 years at the time of T-IPAA were included. Their medical records were retrospectively reviewed. Krickenbeck classification, Cleveland Clinic Incontinence (CCI) score, 36-item Short-form Health Survey Questionnaire, and Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index were used for the evaluation of bowel function and QOL. The median follow-up period was 9.8 years.
Of the 25 patients, 9 had FAP, 9 had UC, and 7 had NFNU. NFNU include 3 of Hirschsprung disease, 2 of intestinal neuronal dysplasia, and 2 of imperforate anus. The median age at T-IPAA was 17.8, 14.2, and 9.3 years for FAP, UC, and NFNU, respectively (p=0.001). Bowel function was satisfactory in terms of voluntary bowel movement (VBM), soiling, and constipation. VBM and constipation were not different between the groups, but soiling was most in NFNU (100%, p=0.047). However, QOL was best in the NFNU group in surveys (p=0.034 and 0.004, respectively).
T-IPAA could be safely applied not only for FAP and UC but also for other diseases in selective cases, with caution.
Citations

Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) is a rare disease that has been reported to occur once in every 25,000 to 50,000 births. According to its etiology, CES is divided into 3 subtypes, tracheobronchial remnants (TBR), fibromuscular hypertrophy (FMH) and membranous diaphragm (MD). Symptoms begin at the weaning period and the introduction of solid food around 6 months with dysphagia and vomiting. Esophagography is first screening test and endoscopic ultrasonography plays important roles to diagnose subtypes deciding therapeutic plan. TBRs were generally treated with surgical resection and end-to-end anasotomosis, whereas FMH and MD had good response rate to endoscopic or radiologic guided dilatation. This article reviews the literature on the etiology, clinical course, diagnosis and management of CES including recent opinion.
Anorectal duplications account for only 5% of gastrointestinal duplications, and cases with involvement of the anal canal are much rarer. Nearly all anorectal duplications are posterior to the rectum; duplications located anterior to the normal rectum are highly unusual, and only a few cases have been reported. We report the case of an anterior anorectocolonic duplication presenting as a rectovaginal fistula in a 2-month-old infant. After diagnosis, the duplication was excised completely without further intestinal complications.
Soft tissue hemangioendothelioma (STHE) is a rare vascular tumor, which has a similar prognosis to borderline malignancy. The disease is poorly understood in pediatric cases because of its low incidence; therefore, we investigated treatment strategies for STHE in children.
We retrospectively analyzed 8 patients with STHE, who were pathologically confirmed between January 1995 and June 2015. The median duration of follow-up was 72 months.
Five were male and the median age at the time of surgery was 1.2 years. Six patients presented with a palpable mass, and 2 patients experienced facial paralysis. The median tumor size was 4.0 cm. The following tumor locations were observed head (2 patients), neck (2 patients), chest wall (1 patient), sacrococcyx (1 patient), upper limb (1 patient), and lower limb (1 patient). The patients underwent either microscopic complete resection (R0) (3 patients), macroscopic complete resection (R1) (2 patients), or macroscopic incomplete resection (R2) (3 patients). After histopathological examination, 6 patients were diagnosed with kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (HE), one with retiform HE, and one with epithelioid HE. Postoperative sequelae occurred as gait disturbance, hearing impairment, and vocal cord palsy. Tumor recurrence or regrowth occurred in 4 patients. These patients underwent reoperation and IFN therapy; however, in the patient with epithelioid HE, metastasis to the scalp occurred after these therapies. The patient with the head tumor who underwent R2 resection, underwent resection three more times, but died 11 months after the first surgery.
When treating STHE in children, R0 resection should be first considered, but recurrence and metastasis should be monitored depending on the size, pathology, and location of the lesion. When major sequelae are expected, function-preserving surgery could be considered, depending on tumor location, size, and nearby organs.
Number of pediatric cholecystectomy has been recently showing a gradually increasing trend. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical features of patients who underwent pediatric cholecystectomy, and the latest trend in cholecystectomy.
In the present study, we conducted a retrospective chart review on 47 patients who had undergone cholecystectomy at a single center. The entire patient population was divided into two groups, according to the time of cholecystectomy (early group, January 1999 to December 2006; late group, January 2007 to August 2014).
The comparison between the early and late groups showed that the number of cholecystectomy increased from 13 to 34 cases representing a 2.6-fold increase. The mean patient age also increased from 5.94±4.08 years to 10.51±5.57 years (p=0.01). Meanwhile, laparoscopic surgery also increased from 15.4% to 79.4%, respectively (p<0.001). However, sex, mean body mass index, comorbidities, indications of cholecystectomy, and previous total parenteral nutrition were not statistically significant.
The results of this study showed that pediatric cholecystectomy cases are increasing, particularly in the 10 to 19 years age group and laparoscopic cholecystectomies are also being performed at an increasing rate. When the patients were compared according to the time of cholecystectomy, there were no differences in other risk factors or indications for cholecystectomy.
Citations

Gastric teratoma is an extremely rare tumor that accounts for less than 1% of all teratomas. Gastric teratoma is mostly presented as a palpable abdominal mass, and is rarely accompanied with gastrointestinal bleeding such as melena or hematemesis. A 5-month-old male infant was brought with a history of pale facial color and dark-colored stool. The hemoglobin level was at 6.1 g/dL, with melena having begun 1 month previous. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy revealed a polypoid mass with bleeding at the upper body and lesser curvature of the stomach. Wedge resection of the stomach was performed and histopathological analysis confirmed the mass to be a mature cystic teratoma. There was no recurrence after the operation during follow-up.
Citations

The duplication of gastrointestinal tract has been known to be a rare condition and two different forms, cystic and tubular type. This study was conducted to examine its clinical characteristics, especially cystic enteric duplication which was detected antenatally or postnatally.
There were 13 patients, who confirmed as cystic enteric duplication after operation between July 1996 and June 2015. Clinical data, including a gender, age at operation, presenting symptoms, diagnostic modalities, locations of lesion, and results of surgical treatment, were reviewed retrospectively according to cases detected antenatally and postnatally.
Five cases were included in antenatal diagnosis group and 8 cases in postnatal diagnosis group. Both groups show slightly common in female and the lesion most common in ileum. Antenatal diagnosis group shows 2 males and 3 females and the mean age at operation was 12±52 days (range, 5 to 90 days). They received operation regardless of symptom. Postnatal group shows 3 males and 5 females and the mean age at operation was 462.5±777.0 days (range, 4 days to 6 years). Moreover, 6 patients (75.0%) were age before 2 years. They usually presented abdominal pain with vomiting.
Cystic enteric duplication could present symptoms at any time during childhood, mainly before 2 years old, and so a proper management should be considered when suspect it. Although it is uncommon, surgical management including a minimal invasive procedure could be attempted despite the neonatal period.
Nodular hidradenoma was diagnosed in a 29-month-old girl on her axilla. Hidradenoma, sometimes designated as acrospiroma, is a benign sweat gland neoplasm, which mostly occurs in adults. Very few cases of hidradenoma have been documented in children in their first decade of life. This case demonstrates that when a child develops a skin nodule, nodular hidradenoma can be a diagnostic option.
Citations

Neonatal neuroblastoma (NBL) is the most common malignant tumor in neonates, but there have been few studies about it. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical features of NBL and to compare prenatal and postnatal diagnosed groups.
Nineteen patients who were diagnosed with NBL prenatally or within 28 days after birth from February 1986 to February 2013 in Seoul National University Hospital were enrolled in the study. The patients were categorized according to the International Neuroblastoma Staging System (INSS) and Children's Oncology Group (COG). Retrospective medical-record reviews were performed on these patients. The operative date, complication, pathological stage, and overall survival of the prenatally diagnosed group and the postpartum diagnosed group were compared.
Tumor was detected via prenatal ultrasonography in 8 patients (42.1%), and 11 patients (57.9%) were diagnosed within 28 days after birth. Based on INSS, the patients were divided into the stage I (n=8), stage II (n=1), stage III (n=3), stage IV (n=4), and stage IVs (n=3) groups, respectively. Based on COG, on the other hand, the patients were divided into the low-risk (n=8), intermediate-risk (n=8), and high-risk (n=3) groups. The postoperative complication rate was 29%. One patient died from complications from chemotherapy. The other 18 patients' mean follow-up period was 77.7 months. The differences between the postoperative complication rate, proportion of early-stage tumor, and overall survival of the prenatal and postnatal groups were not statistically significant (p=0.446, p=0.607, p=0.414).
NBL showed favorable outcomes but relatively higher postoperative complications. There seem to be no significant statistical differences in the postoperative complications, proportion of early-stage tumor, and overall survival between the prenatally diagnosed group and the postpartum diagnosed group.
Immature ganglion cell (IGC) is known for its relationship with intestinal motility and its impact on postoperative functional outcomes of Hirschsprung's disease (HD). There are few studies on the relationship between intestinal dysmotility and IGC in HD patients. 67 patients pathologically diagnosed with HD and who received definitive operation in Seoul National University Children's Hospital from 2010 to 2011 were included. 10 patients were excluded due to inadequate immunohistochemical staining results. The proximal end of resected ganglionic segment was evaluated with immunohistochemistry examination with MAP-2, a marker of ganglionic cells and bcl-2, a marker of IGCs The median age at operation was 155 (15-4678) day-old. 55 (96.5%) patients positive for bcl-2, were regarded as having IGC, and 2 (3.5%) patients positive for MAP-2 but negative for bcl-2, were regarded as having only mature ganglion cells. In the bcl-2 positive group, there were 7 patients (12.7%) with constipation, 15 patients (27.3%) with soiling, 3 patients (5.5%) with perianal excoriation and 6 patients (10.9%) with medication use. In bcl-2 negative group, intestinal dysmotility was not seen. There was no statistical significance in the two groups. Considering that HD is diagnosed at a young age, the rate of IGC present is very high and it might be inappropriate to relate IGC to functional outcome at young ages.
Citations

Citations

Branchial cleft anomalies are the second most common head and neck congenital lesions seen in children. Amongst the branchial cleft malformations, second cleft lesions account for 95 % of the branchial anomalies. This article analyzes all the cases of second branchial cleft anomalies operated on at Seoul National University Hospital from September 1995 to February 2011. We analyzed sex, age, symptom and sign, accompanied anomaly, diagnosis, treatment, pathologic report and outcome via retrospective review of medical records. In this series, we had 61 patients (27 female and 34 male). The mean age at the time of operation was 38 months. 31 lesions were on the right, 20 were on the left and 10 were bilateral. The most frequent chief complaints at presentation were non-tender mass and cervical opening without any discharge. According to anatomic type, 29 patients had branchial cleft sinuses, 14 had cysts, 14 had fistulas and 4 had skin tags. Complete excision was attempted if possible and antibiotics challenged when infection was suspected. Complete excision was achieved in 96.7 % of cases. Incision and drainage was done in 2 cases due to severe inflammation, and both recurred. Postoperative complications included wound infection in 2 cases. Microscopic examonation revealed squamous epithelium in 90.2 % and squamous metaplasia in one case in the branchial cleft cyst wall. In summary, second branchial anomaly is found more frequently on right side of neck. Fistulas are diagnosed earlier than cystic forms. Most cases could be diagnosed by physical examination. The definitive treatment is complete excision and sufficient antibiotics coverage for cases with inflammation. After drainage of infected lesions, follow up excision after 1 year might be beneficial for preventing recurrence.
Congenital diaphragmatic disease is one of the common major congenital anomalies, and its mortality remained still high despite recent medical advances. The aim of this study is to examine the clinical characteristics of congenital diaphragmatic diseases. A total of 39 patients with congenital diaphragmatic disease that underwent surgery from January, 1997 to December, 2009 at Pusan National University Hospital were included in this study. Medical records were retrospectively reviewed. The male to female ratio was 30:9. Six out of 39 cases died (NS) before surgery, 17 patients had Bochdalek's hernia (BH), 11 patients hiatus hernia (HH), 4 diaphragmatic eventration (DE), and 1 Morgagni hernia (MH). There were no differences in mean birth weight and mean gestational age. NS (83.3%). BH (35.3%) was diagnosed more frequently than other diseases in the prenatal period. Three patients (17.6%) of BH expired due to pulmonary hypoplasia and 1 patient had co-existing congenital heart disease. BH was diagnosed more frequently in the prenatal stage and had a higher motality rate than other conditions. Therefore, BH needs to be concentrated more than other anomalies.
Citations

Tapering enteroplasty was first described by Thomas in 1969 as one method of intestinal anastomosis. The advantages of tapering enteroplasty in the intestinal atresia are: First, it makes end-to-end anastomosis possible between the atretic bowel ends with considerable differences in diameters. Second, it promotes the recover of the postoperative bowel function. Third, it prevents the possibility of the short bowel syndrome by eliminating the need of resecting the dilated bowel. A total of 22 patients with intestinal atresia who underwent tapering enteroplasty from January 1988 to December 2005 at our institute were reviewed. In 3 of 22 cases, tapering enteroplasty was the 2nd operation after an initial end-to-oblique anastomosis. We reviewed the following items: age, sex, type and location of intestinal atresia, initial feeding and total enteral feeding start day, the length of hospital stay and complications. The average age of the patients was 7 days. Male to female ratio was 1 to 1.2 (10 cases: 12 cases). We performed the tapering enteroplasty on all types and locations of the intestinal atresia from the duodenum to the colon: type I (n=3), type II (n=4), type IIIA (n=7), type IIIB (n=5), type IIIB and IV (n=1), type IV (n=1) and type C (duodenum) and type IIIB and IV (jejunum). On the average, the oral feeds were started on the postoperative 8.8th day, and full caloric intake via the enteric route was achieved on postoperative 13.3th day. The average length of hospital stay was 19.6 days. There were 1 case (4.5 %) of anastomotic complication and 2 cases (9 %) of adhesive ileus among 22 patients. The tapering enteroplasty on all types of intestinal atresia is a usefull operative method when there are considerable diameter differences between the atretic bowel ends.
Citations

Abnormal distribution of enteric nerves such as adrenergic, cholinergic and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerves (NANC) may cause the failure of relaxation at the involved bowel segment in Hirschsprung's disease (HD). Nitric oxide (NO) is a major inhibitory NANC neurotransmitter in the gastrointestinal tract. NO is synthesized by activation of nNOS (neuronal nitric oxide synthase) in the intramural ganglion cells and regulates bowel movement. To assess the distribution of nNOS in HD, immunohistochemical staining to nNOS was utilized on paraffin embedded specimens. Ten control colon specimens were tested for feasibility of staining. Immunohistochemisrty was done on ganglionic colon as well as aganglionic segment of 15 patients with HD. nNOS immunoreactivity was observed in the neuronal cells, small cells and nerve fibers in the muscle layer and submucosal neuronal cells of control specimens. This finding was also observed in the ganglionic segments of HD. But, there was no nNOS immunoreactivity in aganglionic segments of HD. In conclusion nNOS immunohistochemical staining of paraffin embedded specimen is feasible and reliable. And the results suggest that the relaxation failure of the aganglionic bowel in HD is related to the absence of nNOS containing cells and nerve fibers.
Visceral lipoma originating from the mesentery is very rare in childhood. A 29-month-old male presented with painless abdominal distension. Abdominal ultrasonography and CT revealed a huge multilobulated hypodense mass in the peritoneal cavity. Exploratory laparotomy showed a 26 × 25 × 5 cm sized encapsulated, lobulated, homogenous mass, which originated from the transverse mesocolon. Histologic examination revealed a lipoma. The postoperative course was uneventful.
Citations

Mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver is a rare benign tumor, usually presenting in early childhood. Five children with mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver pathologically verified at Seoul National University Children's Hospital between 1978 and 2000 were analyzed retrospectively. There were two girls and three boys, and their mean age at the operation was 16.0months (range, 4 - 32 months). Three patients presented with abdominal distension. A patient was detected incidentally, and another was detected by prenatal ultrasongraphic examination. Tumor size ranged from 10x8.5cm to 34x29cm. Three tumors were located in the right lobe and two in the left lobe. Four cases underwent complete surgical resection, and the other one underwent incomplete surgical resection and marsupialization. Recurrence or malignant transformation was not noted. Five patients survived without evidence of disease for 35, 36, 38, 142 and 228 months. In conclusion, although mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver is benign lesion, it may be confused, and mixed with embryonal sarcoma. A recent report showed recurrence or malignant transformation after partial excision of the tumor. Therefore, complete excision of the tumor with surrounding normal liver tissue is recommended.
Citations

Ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VP shunt) for hydrocephalus is thought to inhibit the closure of processus vaginalis by increasing intraabdominal pressure, thus it promotes the inguinal hernia. We reviewed the incidence and characteristics of the inguinal hernia in VP shunted patients, and tried to estimate the patency rate of processus vaginalis in early childhood. A reprospective review of patients undergone insertion of VP shunt between January 1980 and May 1998 at Seoul National University Children Hospital was done. 262 patients were included in this study. Among them, 28 patients developed inguinal hernia (10.7%). Six patients developed inguinal hernia before the insertion of VP shunt. According to the age of VP shunt, the inguinal hernia developed in 16.2% (12/74) of patients who had undergone VP shunt before 6 months old, 12.4% (11/89) between 6 months and 2 years old and 5.1% (5/99) after 2 years old. Among 22 patients excluding 6 patients who developed hernia before VP shunt, the incidence of inguinal hernia after VP shunt was 8.6% (22/256) with male predominance (M:F=18:4). 8 patients developed inguinal hernia bilaterally (36.4%). It is suggested that at least 14% of processus vaginalis is patent until 2 years old.
Spontaneous rupture of the eventrated diaphragm is not common. The authors report a case of spontaneous rupture of the congenital diaphragmatic eventration. An 8 year-old girl with right congenital diaphragmatic eventration and nephrotic syndrome was seen in emergency room because of severe abdominal pain and vomiting. She had intermittent abdominal pain for 1 year. Plain chest X-ray and ultrasonography showed entrapped bowels in the right thoracic area. Exploratory laparotomy revealed a ruptured right eventration. THE displaced abdominal viscera were repositioned into the abdominal cavity and the ruptured diaphragm was trimmed and plicated. The postoperative course was uneventful. Only one case of spontaneous rupture of eventrated diaphragmatic has been reported in the English literature.
The WDHA syndrome characterized by watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, and achlorhydria (WDHA syndrome) is rare, and with neurogenic tumors. A 20-month-old girl presenting with symptoms of WDHA syndrome was transferred to our hospital. She had a ganglioneuroblastoma of the adrenal gland. The serum level of VIP was elevated. After complete excision of the tumor, all symptoms related to the WDHA syndrome were relieved and serum VIP level dropped to normal. The postoperative course was uneventful. The patient was treated with postoperative chemotherapy and radiation therapy. There was no evidence of disease 33 months after operation.
Congenital esophageal stenosis (CES) is a narrowing of the esophageal lumen from birth. Three types of CES have been described; tracheobronchial remnants (TBR), membranous web (MW), and fibromuscular stenosis (FMS). We reviewed the clinical features and the surgical outcome of 14 patients, pathologically confirmed as CES. Nine patients had TBR, 3 FMS, and 2 MVV. The mean age at operation was 3.8 years. Five patients were boys and 9 girls. Four patients had other congenital anomalies. Segmental resection of the lesion and end to end anastomosis was utilized in all cases except one who underwent myotomy. The stenotic segment was located at the distal esophagus in all patients. There were 8 complications in 6 patients, but no mortality. The mean follow-up period was 68 months. There were no feeding problems but 3 patients had minor gastroesophageal reflux. Our result indicates that segmental resection and anastomosis is a satisfactory surgical procedure in the management of CES.
Fecal incontinence is not rare in post-op. children who had anorectal malformation, Hirschsprung's disease, and meningomyelocele. It can negatively impact the patient's emotional and social development. Among the options, antegrade continence enema (ACE) was introduced to overcome the demerits in 9 cases from January 1998 to June 1999. All patients have meningomyelocele. The cleanliness and post-operative complications were evaluated. The operative technique has three categories including reversed appendicocecostomy, in situ appendicostomy and neoappendicostomy with cecal flap. All of the patients achieved complete cleanliness. Four patients had post-operative complications. There were two patients with stoma leakage, one with abdominal pain on irrigation and one with stoma stenosis. The leakage was minimal and the pain on irrigation improved spontaneously. The stoma stenosis required revision operation on post-operative 6th month. The ACE has been shown to be safe and highly effective.
Neurocristopathy is characterized as having a common origin in aberrant neural crest development. Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (Ondine's curse) is characterized by marked depression of respiratory drive during sleep and normal ventilation while awake because of no response to both hypercapnea and hypoxia. The girl was full-term, weighing 3020 grams. The girl had poor respiratory effort at birth, but improved with oxygen supply and stimulation. abdominal distention and calcification were noted. During laparotomy transitional zone was found at distal jejunum; a jejunostomy was constructed. Numerous attempts at extubation failed because of apnea. The results of an apnea work-up, including brain sonography, echocardiogram, were normal. The girl died of sepsis at 37 days of age. para-aortic ganglioneuroblastoma was found on autopsy. We experienced a newborn with congenital central hypoventilation syndrome, Hirschsprung's disease and congenital ganglioneuroblastoma representative of neurocristopathy.
Citations

Undifferentiated (embryonal) sarcoma is a rare malignancy of the liver in children and young adults. Seven cases of undifferentiated (embryonal) sarcoma of the liver pathologically verified at Seoul National University Children's Hospital between 1986 and 1999 were retrospectively analyzed. There were three girls and four boys, and their mean age at diagnosis was 12.1 years (range 7–13 years). Six patients presented with an abdominal mass or pain, and one with weight loss. Tumor size ranged from 8.0 × 8.0 cm to 15.0 × 15.0 cm. Four tumors were located in the right lobe, two in the left lobe and one in both. One patient died during chemotherapy. Initial complete resection was accomplished in three patients. Two patients underwent complete resection after chemotherapy. Five patients with complete resection survived without evidence of disease for 8, 11, 13, 28, and 84 months. A patient with partial resection and chemotherapy died of sepsis during chemotherapy 19 months after complete surgical resection. Adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy were performed in all patients after complete surgical resection. In conclusion, though undifferntiated (embryonal) sarcoma of the liver is highly malignant, the combination therapy of surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy appears to result in a favorable prognosis

